Royal Names and Roman Numerals: Why It’s Queen Elizabeth II

When discussing royalty, historical figures, or religious leaders, you might notice names often accompanied by Roman numerals, such as Queen Elizabeth II, King Louis XIV, or Pope John Paul II. These numerals serve an important purpose, clarifying historical lineage and distinguishing one monarch or pope from another. This article explores why Roman numerals are used in royal and papal names, how they’re applied, and why Queen Elizabeth specifically carried the numeral II.
The Purpose of Roman Numerals in Royal Titles
Roman numerals following royal names are used primarily to differentiate rulers with identical first names. This practice clarifies historical references and prevents confusion. Numerals also convey continuity and lineage, emphasizing legitimacy and heritage.
For example, the use of “II” in “Queen Elizabeth II” signifies she was the second monarch in British history with the name Elizabeth, following Queen Elizabeth I, who reigned during the 16th century.
Historical Origin and Usage
The custom of using Roman numerals to denote monarchs dates back centuries, becoming particularly prevalent in European royalty. Historically, kings, queens, and popes took names common in their regions or religions, making numeral designations necessary for clarity.
Early European Examples
One of the most notable historical examples is France, with monarchs named Louis numbered up to Louis XVI, whose reign ended during the French Revolution. England’s use of Roman numerals also dates back centuries, with monarchs such as Henry VIII and Edward VII.
Papal Tradition
Roman numerals also appear in papal names, distinguishing multiple Popes named John, Paul, Benedict, and others. Pope John Paul II, for instance, was the second pope to take the combined names John and Paul.
Why Queen Elizabeth II?
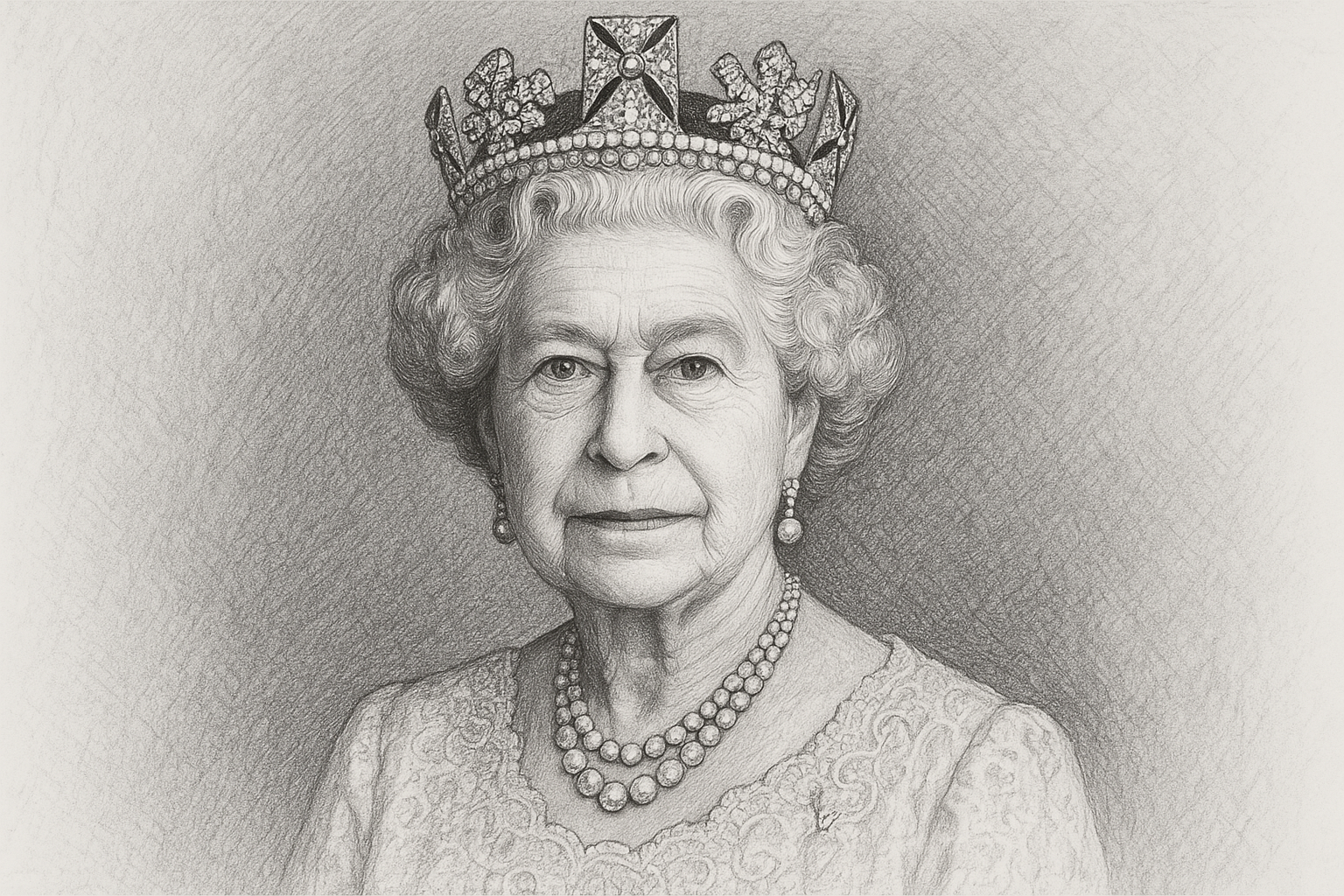
Queen Elizabeth II took the numeral “II” because she was the second English monarch named Elizabeth. Queen Elizabeth I reigned from 1558 to 1603, the last monarch of the Tudor dynasty. Elizabeth I was a significant historical figure, famously known as the Virgin Queen and the ruler who oversaw England’s Golden Age.
Queen Elizabeth II ascended the throne on February 6, 1952, following the death of her father, King George VI. Her choice of numeral honored and acknowledged the legacy and historical impact of her predecessor, reinforcing her position within the continuity of British royal history.
Rules and Controversies Surrounding Numerals
The application of Roman numerals can sometimes lead to disputes or confusion. For example, Queen Elizabeth II’s numeral sparked debate in Scotland because the original Queen Elizabeth (Elizabeth I) ruled only England, not Scotland. Some Scots argued Elizabeth II should have been styled Elizabeth I in Scotland, reflecting different historical lineages before the Acts of Union.
However, official UK policy used “II” across the United Kingdom to maintain consistent royal branding and international recognition.
Numerals and International Royal Families
Roman numerals are also standard in various international royal families, particularly in Europe:
- Spain: King Felipe VI succeeded King Juan Carlos I.
- Sweden: King Carl XVI Gustaf.
- Denmark: Queen Margrethe II.
These numerals provide clarity in global historical discourse, preventing misunderstandings when referencing international monarchies.
Roman Numerals in Cultural Context
Roman numerals have extended their significance beyond mere historical clarity to symbolize tradition, legacy, and authority. In popular culture, films, television, literature, and art regularly reference monarchs and popes with Roman numerals to evoke historical authenticity, formality, and cultural resonance.
Historical Dramas and Media
Historical dramas frequently emphasize numerals to clarify timelines and historical contexts. Shows like “The Crown” prominently feature numerals to distinguish between various historical figures, adding accuracy and depth to storytelling.
Practical Guidelines for Numerals in Royal Titles
When writing or referencing royal titles with Roman numerals, follow these practical guidelines:
- Use uppercase Roman numerals (I, II, III).
- Always place numerals after the name (Elizabeth II, Louis XIV).
- Numerals are typically not pronounced; Queen Elizabeth II is spoken as “Queen Elizabeth the Second.”
Educational and Historical Significance
Understanding the use of Roman numerals in royal and papal names provides educational benefits, enhancing historical literacy and comprehension of cultural contexts. It helps students and history enthusiasts clearly identify and differentiate important historical figures, timelines, and dynastic changes.
Future Use of Roman Numerals in Monarchy
With the accession of new monarchs, Roman numerals continue their significance. For example, upon King Charles III’s accession following Queen Elizabeth II’s passing in 2022, the numeral III clearly marks him as the third monarch of Britain named Charles, distinguishing him from his predecessors, Charles I and Charles II.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do royals choose similar names repeatedly?
Royals often select traditional names associated with successful or revered ancestors to reinforce lineage, legitimacy, and stability.
Are Roman numerals used for every monarch?
Roman numerals are used only when a monarch’s first name repeats a previously used royal name.
Can Roman numerals change if a historical discovery alters lineage understanding?
While theoretically possible, changing numerals due to historical discoveries is extremely rare, given the complexity and widespread historical usage established over time.
Conclusion
Roman numerals play a crucial role in clarifying historical lineages, preserving royal and papal legacies, and maintaining cultural traditions. Queen Elizabeth II’s numeral reflects both historical acknowledgment and practical clarity, highlighting the continuity and heritage of British monarchy. Understanding why and how Roman numerals are used enhances cultural literacy, historical knowledge, and appreciation for the rich legacy of monarchies worldwide.
Explore additional resources on Roman numerals and royal history to deepen your understanding and appreciation of this timeless numerical tradition.